A regenerative brake drives the traction motor to act as an alternator, and converts the kinetic energy produced by the rotation of the tires into electrical energy. The converted electrical energy charges the Li-ion battery.
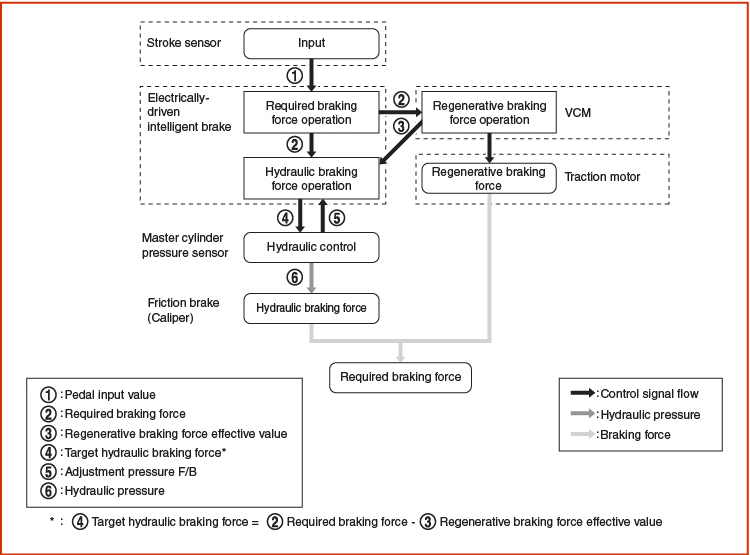
When the brakes are operated (during driving), the electrically driven intelligent brake unit calculates the required braking force based on the input value from the stroke sensor (indicating the amount of brake pedal operation), and then it sends the result to the VCM. At the same time, it calculates the hydraulic braking force needed to produce the required braking force. The 2013 LEAF® recovers more energy from deceleration and braking. It has refined Control Logic that allows it to regenerate energy down to 2 mph (if conditions allow), which is an improvement over the previous 2011-12 LEAF®.
The VCM calculates the regenerative braking force needed to produce the required braking force, and sends the result to the electrically driven intelligent brake unit. At the same time, the traction motor inverter uses the traction motor to perform regenerative braking. An electrically driven intelligent brake is a booster system that generates assist force by using an internal motor to operate a piston inside the master cylinder.
- The Control module is integrated with the electrically driven intelligent brake unit.
The system performs both cooperative control of the regenerative brake and friction brake (same brake as in conventional vehicles) and enables the process of efficient energy recovery. When the brake pedal is depressed during driving, both cooperative control of the braking force from the friction brake (regular brake), and the regenerative brake from the traction motor are used.
- The brake fluid pressure which is applied to each brake caliper is controlled according to the amount of traction motor regeneration. The amount of brake pedal operation is detected according to the signals sent by the stroke sensor, and then sent to the control module of the electrically driven intelligent brake unit.
- Based on the commands from the control module of the electrically-driven intelligent brake unit, the motor inside the electrically driven intelligent brake unit operates and presses the master cylinder piston.
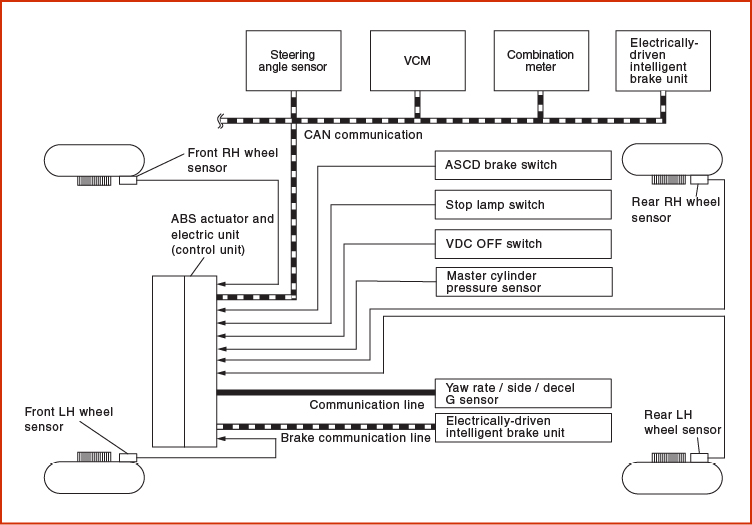
When this occurs, brake fluid is sent to the ABS actuator and electric unit (control unit), which controls VDC, TCS, ABS, EBD, and both brake limited slip differential and brake assist function.
VDC function, TCS function, Brake limited slip differential (BLSD) function and brake assist function are in operation during pressure increases. ABS function and EBD function are in operation during pressure increases.
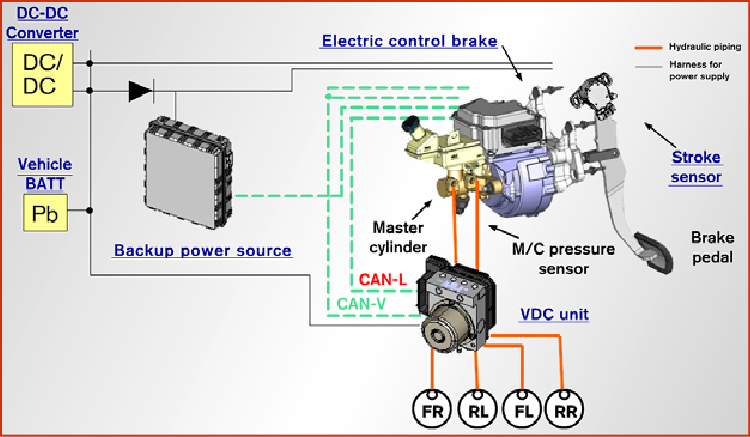
The electrically driven intelligent brake unit calculates the hydraulic braking force based on the regenerative braking force result from the VCM and the calculated result for hydraulic braking force. Based on the calculated result for hydraulic braking force, the electrically driven intelligent brake unit uses the motor inside the electrically driven intelligent brake unit to move the master cylinder piston, adjusting the fluid pressure inside the master cylinder to the master fluid pressure. It also performs adjustment so that the fluid pressure that is actually applied matches the target fluid pressure.
Brake Actuator Operation
When regeneration increases, the piston is retracted by the actuator and hydraulic pressure is reduced. Regeneration reduces before the vehicle stops, and the piston is depressed by the actuator, increasing hydraulic pressure.
On SV and SL models, the B-Mode position replaces the ECO position on the shift position switch. In B position, the VCM provides more “motor” braking force on deceleration by increasing the amount of regenerative braking. The VCM does not limit power usage on acceleration like ECO mode. Like the 2012 model, regeneration will not occur if the Li-ion battery is near the fully charged condition.

Parking Brake
To reduce weight, a foot operated parking brake has been added replacing the e-parking brake. Storage space was added in place of the electric parking brake.